COMPUTER SECURITY
DEFINITION OF COMPUTER SECURITY
Computer security means protecting our computer systems and the information they contain against unwanted access, damage, destruction or modification.We need to protect our computer from any intruders such as hackers, crackers and script kiddie. We do not want strangers to read our e-mail, use our computer to
attack other systems, send forged e-mail from our computer, or examine personal information stored on our computer such as financial statements.
TYPE OF COMPUTER SECURITY
a) HARDWARE SECURITY
Hardware security refers to security measures used to protect the hardware specifically the computer and its related documents.
The examples of security measures used to protect the hardware include PC-locks, keyboard-locks, smart cards and biometric devices.
b) SOFTWARE AND DATA SECURITY
Software and data security refers to the security measures used to protect the software and the loss of data files.Examples of security measures used to protect the software are activation code and serial number.
An example of security measure used to protect the loss of data files is the disaster recovery plan method. The idea of this plan is to store data, program and other important documents in a safe place that will not be affected by any major destruction.
c) NETWORK SECURITY
The transfer of data through network has become a common practice and the need to implement network security has become significant.
Network security refers to security measures used to protect the network system. One example of network security measures is firewall. With firewall, network resources can be protected from the outsiders.
INTRODUCTION COMPUTER THREATS
The computer is a great tool to store important information. In certain cases, the information is very vital that losing it will harm the computer system.
Computer threats can come from many ways either from human or natural disasters. For example, when someone is stealing your account information from a trusted bank, this threat is considered as a human threat. However, when your computer is soaked in heavy rain, then that is a natural disaster threat.
MALICIOUS CODE
Malicious code is also known as a rogue program. It is a threat to computing assets by causing undesired effects in the programmer’s part. The effect is caused by an agent, with the intention to cause damage.
The agent for malicious code is the writer of the code, or any person who causes its distribution. There are various kinds of malicious code. They include virus, Trojan horse, logic door, trapdoor and backdoor, worm and many others.
a) VIRUS
• a program that can pass on the malicious code to other programs by modifying them
• attaches itself to the program, usually files with .doc, .xls and .exe extensions
• destroys or co-exists with the program
• can overtake the entire computing system and spread to other systems
b) TROJAN HORSE
• a program which can perform useful and unexpected action
• must be installed by users or intruders before it can affect the system’s assets
• an example of a Trojan horse is the login script that requests for users’ login ID and password
• the information is then used for malicious purposes
c) LOGIC BOMB
• logic bomb is a malicious code that goes off when a specific condition occurs.
• an example of a logic bomb is the time bomb
• it goes off and causes threats at a specified time or date
e) TRAPDOOR OR BACKDOOR
• a feature in a program that allows someone to access the program with special privileges
f) WORM

• a program that copies and spreads itself through a network
Primary Differences Between Worms And viruses
Worm Virus
Operates through the network Spreads through any medium
Spreads copies of itself as a standalone program Spreads copies of itself as a program that attaches to other
programs
HACKER

Hackers are persons who learn about the computer system in detail. They write program referred to as hacks. Hackers may use a modem or cable to hack the targeted computers.
NATURAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL THREATS
Computers are also threatened by natural or environmental disaster. Be it at home, stores, offices and also automobiles.Examples of natural and environmental disasters:
Flood
Fire
Earthquakes, storms and tornados
Excessive Heat
Inadequate Power Supply
THEFT
Two types of computer theft:
1) Computer is used to steal money, goods, information and resources.
2) Stealing of computer, especially notebook and PDAs.
SECURITY MEASURES
Today, people rely on computers to create, store and manage critical information. It is important that the computer and the data they store are accessible and available when needed. It is also important that users take measures to protect their computers and data from lost, damage and misused.
Security measures mean the precautionary measures taken toward possible danger or damage. There are 6 type of security measures.
1) DATA BACKUP
Data Backup is a program of file duplication. Backups of data applications are necessary so that they can be recovered in case of an emergency.

Depending on the importance of the information, daily, weekly or biweekly backups from a hard disk can be performed.
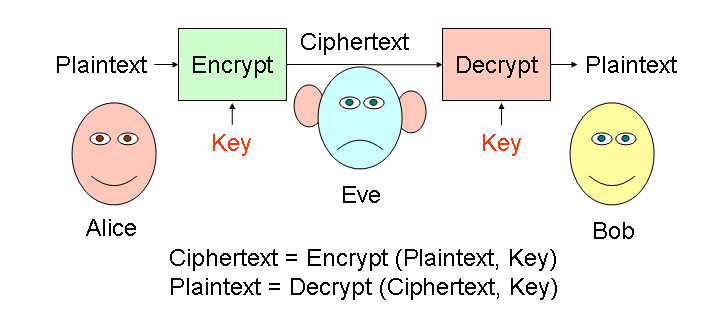
2) CRYPTOGRAPHY
Cryptography is a process of hiding information by altering the actual information into different representation.
Almost all cryptosystems depend on a key such as a password like the numbers or a phrase that can be used to encrypt or decrypt a message. The traditional type of cryptosystem used on a computer network is called a symmetric secret key system.
3) ANTIVIRUS
An antivirus program protects a computer against viruses by identifying and removing any computer viruses found in the computer memory, on storage media or incoming e-mail files.
An antivirus program scans for programs that attempt to modify the boot program, the operating system and other programs that normally are read from but not modified.
4) ANTI-SPYWARE
Spyware is a program placed on a computer without the user’s knowledge. It secretly collects information about the user. The spyware program communicates information to the outside source.
An anti-spyware application program sometime called tracking software or a spybot is used to remove spyware.Among of the popular anti-spyware programs are:
• Spybot Search and Destroy
• Ad-aware
• Spyware Blaster
5) FIREWALL
Firewall is a piece of hardware or software which functions in a networked environment to prevent some communications forbidden by the security
policy.
Firewall implement a security policy. It might permit limited access from in or outside the network perimeters or from certain user or for certain activities.
6) HUMAN ASPECTS OF SECURITY MEASURES
Human aspects refer to the user and also the intruder of a computer system. It is one of the hardest aspects to give protection to. The most common problem is the lack of achieving a good information security procedure.